Discover the fascinating world of quantum mechanics with easy-to-understand guides like Quantum Physics For Dummies. Perfect for beginners, these resources simplify complex concepts without heavy math.

What Is Quantum Mechanics?
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that studies the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales, such as atoms, subatomic particles, and even light. It challenges classical physics by introducing concepts like wave-particle duality, where particles can act as both waves and particles. Quantum mechanics also relies on probabilities rather than definite outcomes, as described by the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle. This theory explains phenomena like superposition and entanglement, where particles can exist in multiple states or be connected across vast distances. It forms the basis for modern technologies like transistors, lasers, and computer chips. Understanding quantum mechanics requires a shift from everyday intuition to a probabilistic worldview.
Why Quantum Mechanics Matters
Quantum mechanics is crucial for understanding the behavior of matter and energy at atomic and subatomic levels; It has led to groundbreaking technologies like semiconductors, lasers, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which are integral to modern life. Quantum principles enable the development of transistors, essential for computers and smartphones, and underpin advancements in fiber optics and the internet. Emerging technologies such as quantum computing and quantum cryptography rely on these principles, promising revolutionary solutions in fields like cryptography, drug discovery, and artificial intelligence. Additionally, quantum mechanics enhances our understanding of the universe, from black holes to molecular biology, inspiring scientific and economic progress. Its applications are vast, impacting everything from healthcare to telecommunications, making it a cornerstone of modern innovation and discovery.
A Brief History of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics emerged in the early 20th century as a revolutionary approach to understanding the atomic and subatomic world. In 1900, Max Planck introduced the concept of quantized energy, laying the foundation. Albert Einstein further developed this idea by explaining the photoelectric effect using light quanta in 1905. Niels Bohr’s model of the atom in 1913 and Louis de Broglie’s wave-particle duality in 1924 were pivotal. The 1920s saw Erwin Schrödinger’s wave mechanics and Werner Heisenberg’s matrix mechanics, unifying quantum theories. By the 1930s, quantum mechanics was established, with the Copenhagen interpretation by Bohr and Heisenberg dominating. This period transformed physics, reshaping our understanding of reality at the smallest scales.

Basic Concepts of Quantum Physics
Quantum physics explores phenomena like wave-particle duality, superposition, and entanglement. These concepts explain how particles behave at microscopic scales, challenging classical physics understanding.
The Wave-Particle Duality
In quantum physics, wave-particle duality is a fundamental concept that describes how particles like electrons and photons can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. This idea, introduced by Einstein and de Broglie, challenges classical notions of matter and energy. For instance, the double-slit experiment shows that particles can create interference patterns like waves but can also be observed as discrete particles. This duality is central to understanding quantum behavior, as it explains how particles can behave differently depending on how they are observed. Resources like Quantum Physics For Dummies and related PDF guides provide simplified explanations of this phenomenon, making it accessible to beginners.
Quantum Superposition
Quantum superposition is a mind-bending concept where particles exist in multiple states simultaneously until measured. Imagine a coin that’s both heads and tails at the same time—this is how particles like electrons and photons can exist in overlapping states. This phenomenon, described in guides like Quantum Physics For Dummies, challenges classical logic but is fundamental to quantum mechanics. For example, Schrödinger’s cat thought experiment illustrates superposition, where the cat is both alive and dead until observed. This principle is crucial for understanding quantum behavior and is a cornerstone of quantum computing, enabling qubits to process vast amounts of information simultaneously. Superposition highlights the strange yet powerful nature of quantum reality.
Quantum Entanglement
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where two or more particles become interconnected, regardless of distance; When something happens to one particle, the other instantly reacts, even if separated by billions of miles. This “spooky action at a distance,” as Einstein called it, defies classical physics. Guides like Quantum Physics For Dummies explain that entangled particles share states like spin or polarization. For example, if one electron is measured as “up,” its entangled partner will be “down,” no matter the distance. This phenomenon has practical applications in quantum cryptography and teleportation, making it a cornerstone of quantum communication. Entanglement revolutionizes our understanding of reality and connectivity in the quantum world.
The Uncertainty Principle
The Uncertainty Principle, formulated by Werner Heisenberg, states that it’s impossible to simultaneously know both the exact position and momentum of a particle. This fundamental concept in quantum mechanics reveals the inherent limitations of measurement at the subatomic level. The principle implies that the act of observing a particle disturbs its state, making precise measurements unattainable. For example, shining light to locate a particle alters its momentum. This idea challenges classical notions of determinism and introduces probabilistic interpretations of physical phenomena. Guides like Quantum Physics For Dummies simplify this complex concept, emphasizing its profound implications for understanding the behavior of matter and energy at the quantum scale.

Key Principles of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics relies on core principles like wave-particle duality, superposition, and entanglement. These concepts, explained in resources like Quantum Physics For Dummies, form the foundation of quantum theory.
Schrödinger Equation
The Schrödinger Equation is a fundamental equation in quantum mechanics that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes over time. It is central to understanding wave mechanics and predicting the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic level. This equation, formulated by Erwin Schrödinger, is essential for calculating probabilities in quantum systems. Resources like Quantum Physics For Dummies simplify the equation’s complexity, explaining its role in determining wavefunctions and energy states. By solving the Schrödinger Equation, scientists can model quantum phenomena, making it a cornerstone of modern physics and its applications in technology and research.
Wavefunction and Probability
The wavefunction is a mathematical description of a quantum system, encapsulating all possible information about its state. In simple terms, it’s like a map that tells us where a particle might be and how it might behave. According to the principles outlined in Quantum Physics For Dummies, the square of the wavefunction’s amplitude gives the probability of finding a particle in a specific location. This probabilistic nature is a cornerstone of quantum mechanics, explaining why particles don’t follow definite paths but instead exist in a realm of possibilities until measured. Understanding wavefunctions and their connection to probability is key to grasping the unpredictable yet structured world of quantum physics.
Quantum Tunneling
Quantum tunneling is a mind-bending phenomenon where particles pass through solid barriers that classical physics deems impenetrable. Imagine a ball rolling up a hill; if it doesn’t have enough energy to go over, it normally rolls back. But in quantum mechanics, the ball can “tunnel” through the hill. This effect, explained in Quantum Physics For Dummies, arises because particles exist as probability waves, allowing them to “leak” into forbidden regions. Tunneling is crucial in technologies like scanning tunneling microscopes and flash memory. It defies intuition but is a cornerstone of quantum behavior, showing how particles can defy classical expectations in surprising ways.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, formulated by Werner Heisenberg, states that it’s impossible to simultaneously know both the exact position and momentum of a particle. This fundamental concept challenges classical physics, where precise measurements were believed possible. The principle suggests that the act of measurement inherently disturbs the system, introducing uncertainty. For example, shining light to locate a particle alters its momentum. This idea underscores the probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics, where predictions rely on likelihoods rather than exact outcomes. As explained in Quantum Physics For Dummies, this principle is a cornerstone of modern physics, revealing the intrinsic limitations of measuring subatomic particles and shaping our understanding of reality at the quantum level.
Quantum Mechanics in Everyday Life
Quantum mechanics influences modern technology, from semiconductors in electronics to MRI machines in medicine. It powers advancements in computing, communication, and security, shaping our daily lives invisibly.
Applications in Technology
Quantum mechanics has revolutionized modern technology, enabling breakthroughs like transistors, lasers, and semiconductors. These components power everything from smartphones to computers. Quantum computing leverages qubits for faster processing, solving complex problems in cryptography, drug discovery, and optimization. Quantum cryptography enhances data security through unbreakable encryption, safeguarding communication networks. Even everyday items like memory chips and solar panels rely on quantum principles. The impact extends to medical imaging, with MRI machines using quantum phenomena to create detailed body scans. These advancements demonstrate how quantum mechanics drives innovation, transforming industries and improving daily life. Understanding these applications through resources like Quantum Physics For Dummies makes the science accessible to everyone.
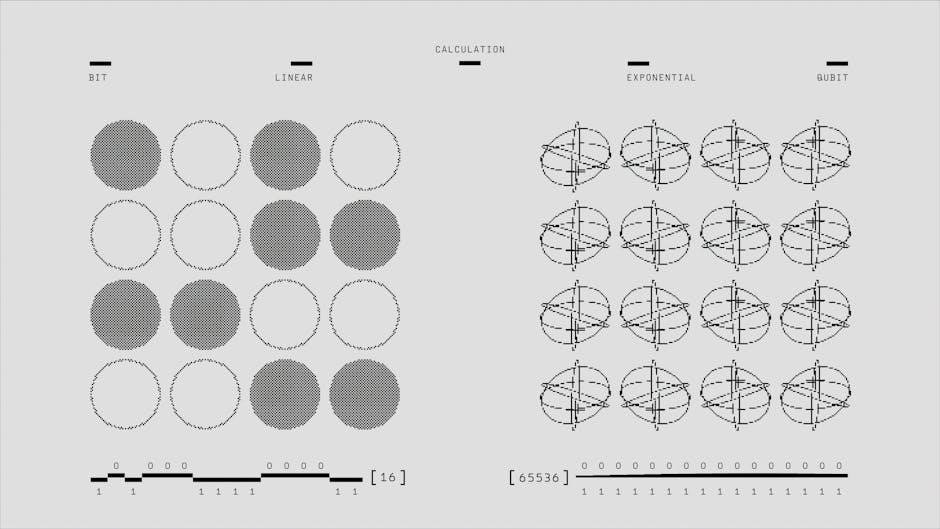
Quantum Computing Basics
Quantum computing is a revolutionary technology that leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations exponentially faster than classical computers for specific tasks. At its core, quantum computing uses qubits (quantum bits), which, due to superposition, can exist in multiple states simultaneously—unlike classical bits, which are either 0 or 1. This allows quantum computers to process vast amounts of information in parallel, making them particularly powerful for problems like factoring large numbers, simulating molecular structures, and optimizing complex systems.
Entanglement is another key feature, where qubits are interconnected, enabling operations on multiple qubits at once. Quantum gates, the quantum equivalent of logic gates, manipulate qubits to perform calculations. While quantum computing holds immense potential, especially in cryptography and drug discovery, understanding its basics requires grappling with quantum mechanics concepts like wave functions and probabilities. Resources like Quantum Mechanics for Dummies can provide an accessible introduction to these foundational ideas, helping beginners build a solid understanding of quantum computing principles.

Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography uses quantum mechanics to secure communication, ensuring data remains confidential. It relies on the principles of quantum entanglement and superposition, where any attempt to measure or eavesdrop on the communication disrupts the system, making it detectable. This technology enables the creation of unbreakable encryption keys, known as quantum key distribution (QKD), which are used to encode and decode messages. QKD ensures that even if an unauthorized party tries to intercept the key, it introduces errors, alerting both the sender and receiver to the breach. Quantum cryptography is particularly valuable for sensitive applications like financial transactions, military communications, and secure data transfer, promising a future of ultra-secure information exchange. Resources like Quantum Mechanics for Dummies provide an introduction to these cutting-edge security methods.
Quantum Mechanics in Medicine
Quantum mechanics plays a transformative role in advancing medical science, offering innovative solutions for diagnosis, treatment, and research. Technologies like MRI and PET scans rely on quantum principles to create detailed images of the body. Quantum dots, tiny particles with unique optical properties, are used for precise drug delivery and cancer treatment. Additionally, quantum computing accelerates drug discovery by simulating molecular interactions, reducing development time and costs. Quantum sensing enhances the accuracy of medical diagnostics, enabling earlier detection of diseases. These applications, explained in resources like Quantum Mechanics for Dummies, demonstrate how quantum science is revolutionizing healthcare, leading to more effective and personalized treatments. The integration of quantum technologies promises a future of faster, more accurate, and life-saving medical solutions.

Learning Resources for Beginners
Explore Quantum Mechanics For Dummies and Quantum Physics For Dummies for clear introductions. Online courses, PDF guides, and video explainers provide hands-on learning opportunities for newcomers to the field.
Recommended Books for Dummies
For beginners, Quantum Physics For Dummies by Steven Holzner is a top choice, offering a clear and engaging introduction to quantum mechanics. Quantum Mechanics For Dummies provides a comprehensive yet accessible overview, perfect for those new to the subject. Both books avoid heavy math, focusing on conceptual understanding. They cover key topics like wave-particle duality, superposition, and entanglement in a way that’s easy to digest. These resources are ideal for students or enthusiasts looking to build a solid foundation without getting overwhelmed. They also include practical examples and real-world applications, making complex ideas relatable. Whether you’re studying or just curious, these books are excellent starting points for your quantum journey.

Online Courses and Tutorials
Explore a variety of online courses and tutorials designed to make quantum mechanics accessible to everyone. Platforms like edX and Coursera offer structured courses that simplify complex concepts, often mirroring college-level curricula but tailored for beginners. Khan Academy and YouTube channels provide free, engaging tutorials that break down quantum principles into digestible lessons. Many of these resources avoid heavy math, focusing on conceptual understanding. For example, “Quantum Mechanics for Dummies” courses are available online, offering step-by-step guides to topics like superposition and entanglement. These platforms are perfect for those seeking a flexible learning experience, allowing you to grasp the fundamentals at your own pace. They’re ideal for students or enthusiasts looking to explore quantum mechanics without prior expertise.
PDF Guides and Worksheets
Enhance your learning journey with an array of free and accessible PDF guides and worksheets tailored for beginners exploring quantum mechanics. These resources provide a structured approach to understanding complex concepts, often complemented by practical exercises and examples. From foundational topics like wave-particle duality to advanced ideas such as quantum entanglement, these PDFs are designed to simplify the learning process. Many guides, such as Quantum Physics For Dummies and Quantum Mechanics For Beginners PDF, offer clear explanations and step-by-step problem-solving techniques. Worksheets allow you to test your knowledge and apply theoretical concepts in real-world scenarios. Perfect for self-paced learning, these resources are invaluable for students and enthusiasts alike, offering a comprehensive yet approachable pathway to mastering quantum mechanics.
Video Lectures and Explainers
Video lectures and explainers are an excellent way to grasp quantum mechanics in an engaging and visual format. Platforms like YouTube and educational websites offer a wealth of free and paid content tailored for beginners. Channels such as 3Blue1Brown and Crash Course provide animated explanations that simplify complex concepts like superposition and entanglement. Additionally, university courses and TED Talks often cover quantum mechanics in an accessible manner. These videos are perfect for visual learners who prefer seeing ideas illustrated rather than just reading about them. They also serve as a great supplement to books like Quantum Physics For Dummies, offering a dynamic learning experience that makes the subject both fun and approachable.


Advanced Topics in Quantum Mechanics
Explore Quantum Field Theory, Relativity, Many-Worlds Interpretation, and Quantum Consciousness for deeper insights into the subject, building on foundational knowledge from resources like Quantum Physics For Dummies.
Quantum Field Theory
Quantum Field Theory (QFT) is an advanced framework that merges quantum mechanics with relativity, describing particles as excitations of underlying fields. It explains phenomena like particle creation and annihilation, and is foundational to modern particle physics.
Resources like Quantum Mechanics For Dummies introduce QFT concepts, providing a bridge for learners to transition from basic quantum principles to more complex theories.
QFT is essential for understanding the Standard Model of particle physics and remains a cornerstone of theoretical physics research and applications.
Relativity and Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics and relativity are two pillars of modern physics, but they describe different realms: quantum mechanics focuses on tiny particles, while relativity deals with spacetime and gravity.
The challenge lies in unifying these theories, as they conflict under extreme conditions, such as black holes or the early universe.
Efforts to merge them have led to theories like quantum gravity and string theory, though a complete solution remains elusive.
Resources like Quantum Physics For Dummies provide insights into these concepts, helping learners grasp their significance and the ongoing quest for a unified theory.
Many-Worlds Interpretation
The Many-Worlds Interpretation (MWI) is a mind-bending concept in quantum mechanics proposing that every quantum decision spawns parallel universes. Each universe represents a different outcome, resolving paradoxes like Schrödinger’s cat. This theory, controversial among scientists, suggests an infinite number of universes to explain quantum probabilities. While some find it hard to accept due to the sheer scale, it offers a unique perspective on quantum mechanics. Books like Quantum Physics For Dummies explore MWI, making it accessible for learners to grasp without technical complexity. This interpretation challenges our understanding of reality, sparking curiosity and debate in the scientific community. It remains a fascinating topic in quantum discussions, inviting further exploration and understanding.
Quantum Consciousness
Quantum consciousness explores the intriguing idea that quantum mechanics plays a role in the human mind. It suggests that quantum processes like superposition and entanglement might influence consciousness. This theory proposes that the brain’s quantum states could enable unique cognitive functions, such as intuition or creativity. While controversial, it challenges the view of consciousness as purely classical. Books like Quantum Physics For Dummies introduce these concepts simply, making them accessible to new learners. Quantum consciousness remains a speculative yet fascinating area, blending physics and philosophy to understand the nature of mind and reality. It inspires curiosity and debate among scientists and philosophers alike.
Quantum mechanics for dummies resources offer a solid foundation, simplifying complex concepts for beginners. Explore these guides to deepen your understanding and spark further curiosity in quantum physics.
Recap of Key Concepts
Quantum mechanics introduces groundbreaking ideas that reshape our understanding of the physical world. Key concepts include wave-particle duality, where particles exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior, and quantum superposition, where particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously. Quantum entanglement demonstrates how particles can be instantaneously connected, regardless of distance. The uncertainty principle highlights the fundamental limits of measuring certain properties, like position and momentum, simultaneously. Additionally, Schrödinger’s equation and the concept of wavefunctions are central to understanding quantum systems. These principles form the foundation of quantum theory and its applications in modern technology.
Future of Quantum Mechanics
The future of quantum mechanics is promising, with advancements in quantum computing and quantum technology leading the way. These innovations could revolutionize fields like cryptography, materials science, and artificial intelligence. Quantum computing aims to solve complex problems beyond classical computers’ capabilities, while quantum cryptography offers unhackable communication methods. Research into quantum field theory and relativistic quantum mechanics may unify quantum principles with general relativity. As these technologies mature, they could transform industries and create new opportunities. The study of quantum mechanics remains a vibrant and evolving field, promising breakthroughs that will shape the 21st century and beyond.
Encouragement for Further Learning
Diving into quantum mechanics can seem daunting, but with the right resources, it becomes an exciting journey. Start with Quantum Physics For Dummies or similar beginner-friendly guides to build a solid foundation. Explore online courses and video lectures that break down complex concepts visually. Engage with communities and forums where enthusiasts share insights and solve problems together. Remember, quantum mechanics is a field that rewards curiosity and persistence. As you progress, you’ll uncover its beauty and relevance to cutting-edge technologies. Embrace the challenge and enjoy the adventure of understanding the quantum world!
